Quality assurance of food products
The quality of food for human consumption is determined by the safety and quality of the entire food chain. From farm to fork, food safety falls under the responsibility of each element involved: farmer/farmer, transporter, processor, retail store, institutions responsible for checking and controlling food safety.
The reputation of the processing company or restaurant is correlated with the application of food safety standards.
In a food production facility or restaurant, the incorrect management of food safety standards brings a major risk to the health of consumers
Food contaminated with bacteria can cause illnesses with serious consequences. As a rule, these diseases produced by bacteria are accompanied by severe diarrheal conditions, which can lead to other disorders. And in the case of children, they can even be fatal.
Hygiene monitoring in the food industry is an extremely important factor.
Some bacteria can multiply up to 1,000 times in just 2 hours.
Food, especially unwashed or thermally prepared for too short a time, can contain bacteria that affect our health. Cross-contamination of food refers to the transfer of bacteria or other microorganisms from one substance to another. Cross-contamination can occur in food, but also allergens, chemicals and toxins. Applying food contamination prevention measures is the best way to maintain food safety and consumer health. The specifications according to Order 976/1998 and also Reg. (EC) 2073/2005 as amended.

Food safety standards
- SR EN ISO 7218 - microbiology of food and feed. general requirements and guidelines for microbiological examinations.
- SR EN ISO 8199 - quality of water. general requirements and guidelines for microbiological examinations on culture medium.
If food safety standards are mismanaged, the risk of endangering the health of customers is maximum and the reputation of the processor or restaurant is severely damaged.
Types of bacteria that cause the most illness in the population
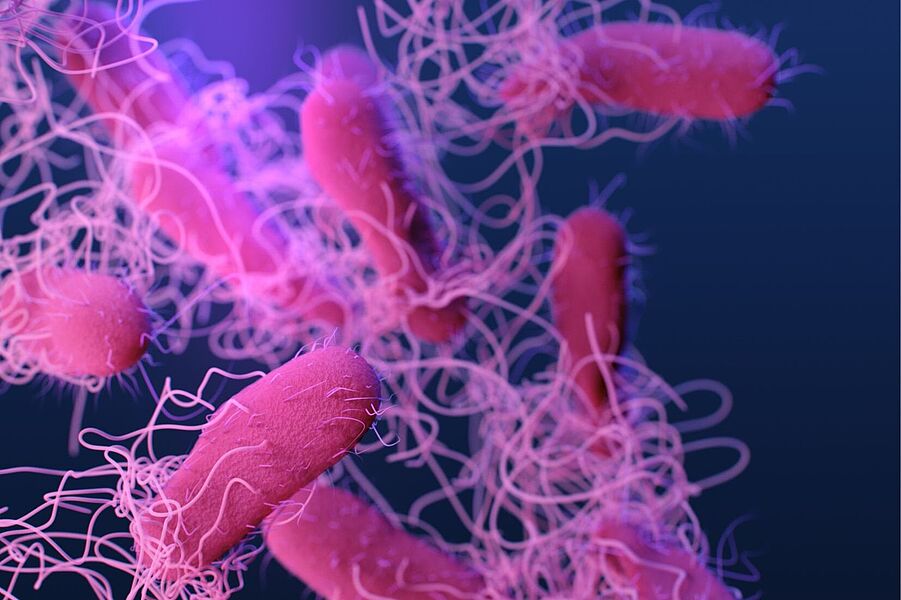
E.coli is found especially in undercooked beef, unpasteurized milk, cheese made from raw milk, raw fruits and vegetables, from contaminated water, directly from animals such as cows, sheep or goats.
Listeria can be taken from catering products, unpasteurized milk, cheese made from raw, unpasteurized milk, smoked and refrigerated fish or seafood, raw vegetable roots.
Clostridium perfringens can be found in beef, meat and chicken products, certain sauces.
Laboratory testing methods
- Horizontal method for the detection and enumeration of Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria spp
- The horizontal method for the detection of Salmonella spp
- Horizontal method for counting Escherichia coli
- Horizontal method for counting Enterobacteriaceae
- Detection and counting of anaerobic sulfite-reducing bacteria (Clostridia) spores
WESSLING Romania performs analyzes based on national and European standards. Analyzes are performed with accredited methods by RENAR and authorized by the Ministry of Health and/or the Environment. More than 20 years of professionalism are put in the service of health insurance.
Conact person
- Veronica Dumitru
- +4 0728 293 555
- food@wessling.ro



